How to Pick a True Biodegradable Plastic Bag? 3 Key Indicators
In the fight against plastic pollution and in an effort to find sustainable alternatives, many consumers have begun using “biodegradable plastic bags”. However, the market is flooded with many products that do not live up to their name. In order to make sure you're making a truly eco-friendly choice, it's crucial to know how to recognize a true biodegradable plastic bag. Here are three key indicators to look for.
Indicator 1: Material Composition
The primary factor in determining the authenticity of a biodegradable plastic bag is its material composition. Genuine biodegradable plastic bags are usually made from polymers that can be broken down by microorganisms in the environment. Common materials include polylactic acid (PLA), polybutylene adipate (PBAT) and starch-based polymers.

PLA is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugar cane and is a popular choice for biodegradable products. It has good mechanical properties and can be processed like traditional plastics. On the other hand, PBAT is a polyester copolymer with excellent flexibility and toughness. When combined with PLA or starch, it improves the overall performance of biodegradable plastics.

Be wary of bags that claim to be biodegradable but contain large amounts of non-biodegradable polymers such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These non-biodegradable components can prevent the bags from breaking down completely, causing long-term environmental pollution. A study by the University of California found that many of the so-called “biodegradable” bags on the market actually contain up to 30% non-biodegradable materials and are therefore ineffective in reducing plastic waste.
Indicator 2: Certification and Standards Compliance
Assurance of the quality and biodegradability of plastic bags depends on their proper certification and compliance with recognized standards. In the United States, ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials) has developed standards for biodegradable plastics. For example, ASTM D6400 specifies requirements for compostable plastics, including a biodegradation rate of at least 90% within six months under specific composting conditions.
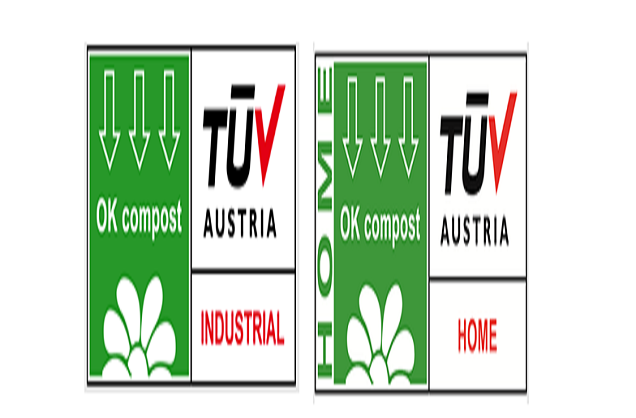
In Europe, the EN 13432 standard is widely recognized. This standard covers not only the biodegradability of the material, but also its ability to decompose in a composting environment and the absence of harmful residues. Bags complying with this standard can be labeled with the European Biodegradable Plastics Association (EBio) logo.

Certification by independent third-party organizations such as TÜV SÜD or Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provides additional assurance. These organizations conduct rigorous tests to verify that the product meets the required biodegradability criteria. The importance of relying on these verified labels is underscored by a recent survey showing that only about 40% of products labeled as biodegradable in a sample of major retailers had actually received proper third-party certification.
Indicator 3: Biodegradation rate and environmental impact
The rate of biodegradation of plastic bags is an important indicator of their effectiveness. A truly biodegradable plastic bag should break down relatively quickly in an appropriate environment (e.g., composting facility or natural soil). The rate of biodegradation is usually measured as the percentage of material that is converted by microorganisms into carbon dioxide, water and biomass in a given period of time.

According to international standards, high-quality biodegradable plastic bags should achieve a biodegradation rate of at least 60% within six months in a laboratory environment that simulates composting conditions. In the real world, biodegradation rates may vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity and the presence of microorganisms. However, bags that show little to no degradation over a longer period of time are likely not truly biodegradable products.
In addition to the biodegradation rate, it is important to consider the overall environmental impact of bag production and disposal. Biodegradable plastic bags made from renewable resources typically have a lower carbon footprint than traditional plastic bags. They also do not release harmful chemicals or microplastics into the environment during the degradation process, which reduces the risk of contamination of soil, water and wildlife.
 Significant progress in PBAT/s
Significant progress in PBAT/s
 PLA/PBAT composite film degrad
PLA/PBAT composite film degrad
 A New Choice for Takeaway Pack
A New Choice for Takeaway Pack
 Significant progress in PBAT+s
Significant progress in PBAT+s
CONTACT
Add: Room 4006, No.1 Helong Yiheng Road, Baiyun District, Guangzhou City
Tel: +8613450255948
Wechat : +86-13450255948
Fax: +86-13450255948
E-mail: 13450255948@163.com








